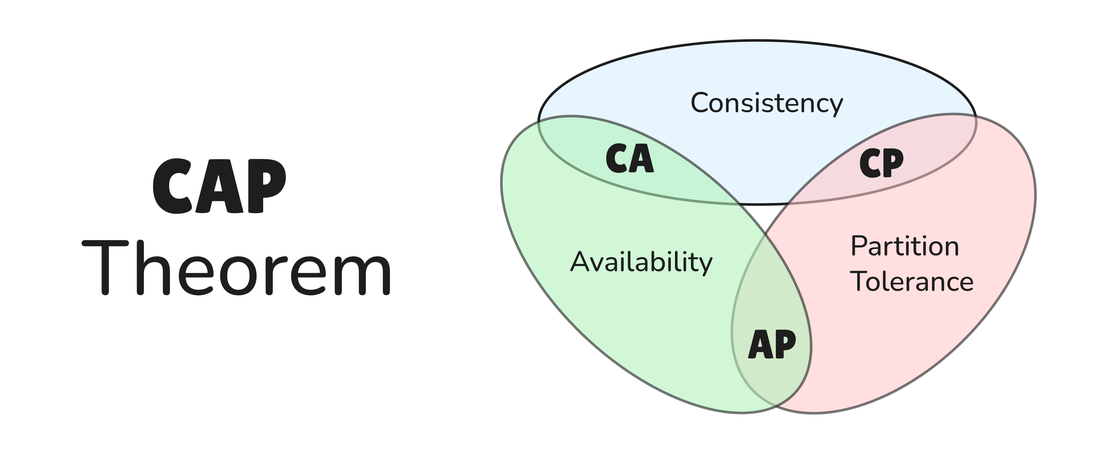
The CAP Theorem: Navigating the Inevitable Trade-Off in Distributed Systems
The CAP Theorem, also known as Brewer’s Theorem, stands as a cornerstone in the architecture of distributed systems. It articulates a fundamental constraint: it is impossible for a distributed data store to simultaneously guarantee Consistency, Availability, and Partition Tolerance. In the face of an unavoidable network partition, a system is compelled to sacrifice either strong consistency or continuous availability.
Read More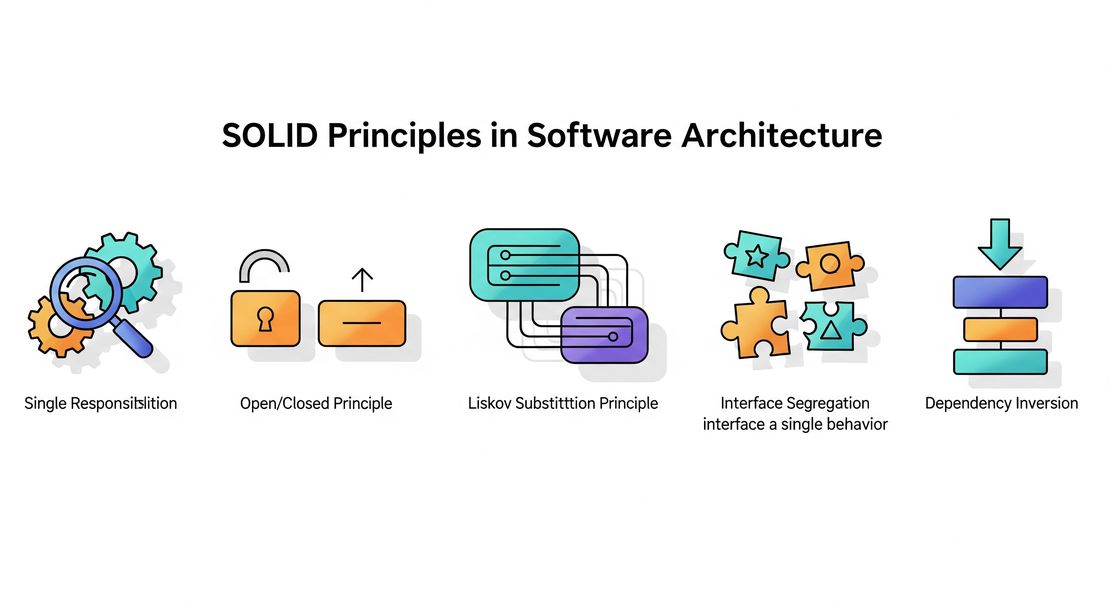
SOLID Principles in Software Architecture
In the field of software architecture and engineering, the SOLID principles provide a foundational framework for creating robust, scalable, and maintainable systems. These principles help reduce coupling, improve cohesion, and make codebases easier to test and evolve.
Read More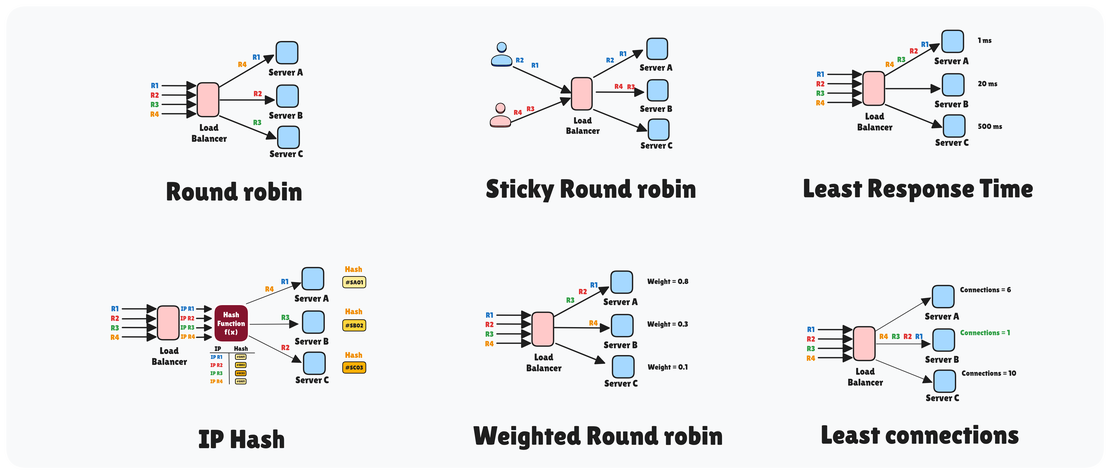
Load Balancing Algorithms: A Comprehensive Guide
Load balancing is a crucial technique in distributed systems and network architecture, designed to enhance the availability, reliability, and scalability of services. It involves distributing incoming network or application traffic across multiple servers to ensure that no single server becomes a bottleneck or point of failure. By intelligently routing requests, load balancing helps optimize resource use, maximize throughput, minimize response time, and avoid overload on any single server.
Read More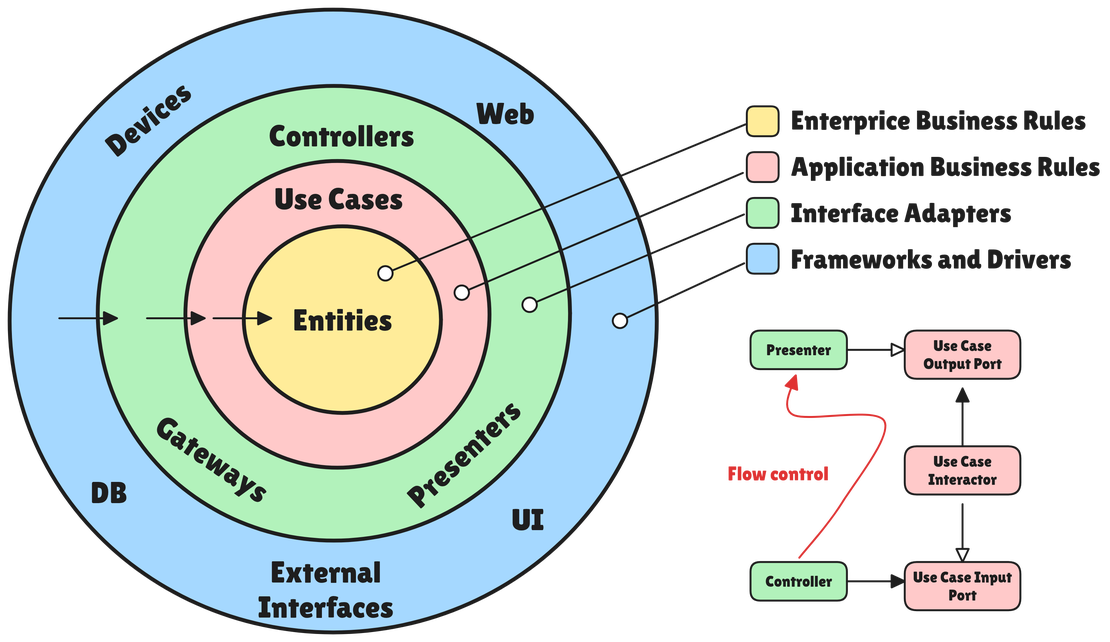
Clean Architecture: Building Robust and Maintainable Software
In the ever-evolving landscape of software development, building applications that are not only functional but also adaptable, testable, and maintainable is paramount. This is where Clean Architecture comes into play. More than just a set of rules, Clean Architecture is a philosophy that guides the structuring of software systems to ensure they remain flexible and resilient in the face of changing requirements. It emphasizes the separation of concerns, allowing different parts of the system to evolve independently without impacting the core business logic. This article will delve into the intricacies of Clean Architecture, exploring its history, core principles with real-world examples, and practical implementations across various programming languages.
Read More