UMAP: The Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection Algorithm
UMAP (Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection) is a cutting-edge, non-linear dimensionality reduction technique. Its primary purpose is to map high-dimensional data into a lower-dimensional space (typically 2D or 3D) while faithfully preserving the topological structure of the data. It is often preferred over t-SNE for its faster runtime and its ability to preserve both local and global data structure more effectively.
Read More
Getting starter with Apache Airflow
Setting up Apache Airflow with Docker is the recommended and easiest way to get started, especially for local development. Docker isolates Airflow and its dependencies in containers, preventing conflicts with your host machine and ensuring a reproducible environment.
Read More
Data Augmentation for Text Corpus Generation: Enhancing NLP Models with Synthetic Data
Data augmentation has revolutionized various fields, especially computer vision, by artificially expanding datasets and improving model generalization. While widely adopted for image data, its application to text, particularly for corpus generation, presents unique challenges and opportunities. As a Natural Language Processing (NLP) expert, I will delve into the data augmentation techniques for text corpus generation, providing scientific backing, illustrative examples, and practical Python implementations.
Read More
How to Determine If a Dataset Is Small or Big
In the data science world, terms like “small dataset” and “big dataset” are commonly used, but surprisingly, they lack universal definitions. Determining whether a dataset is “small” or “big” depends on several contextual factors: the analytical task, the computing environment, and even the underlying structure of the data.
Read More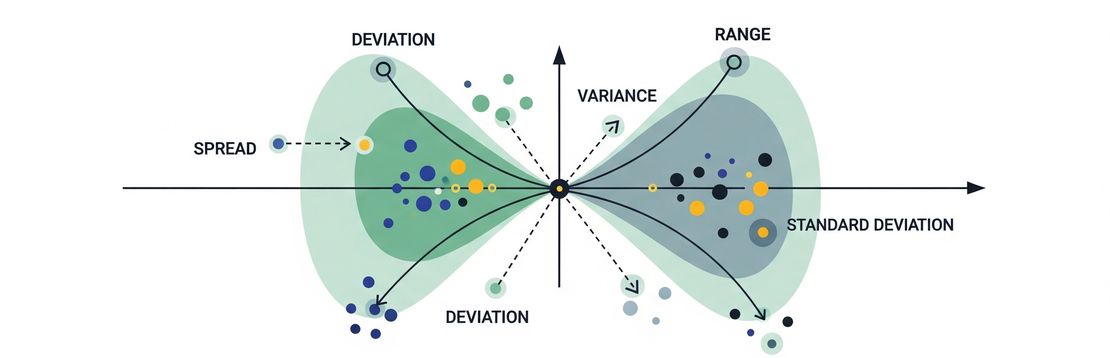
Measures of dispersion
Measures of dispersion quantify how much data values vary or spread out. Understanding dispersion helps you grasp the reliability, consistency, and variability of data.
Read More