Algorithms
- Home /
- Categories /
- Algorithms
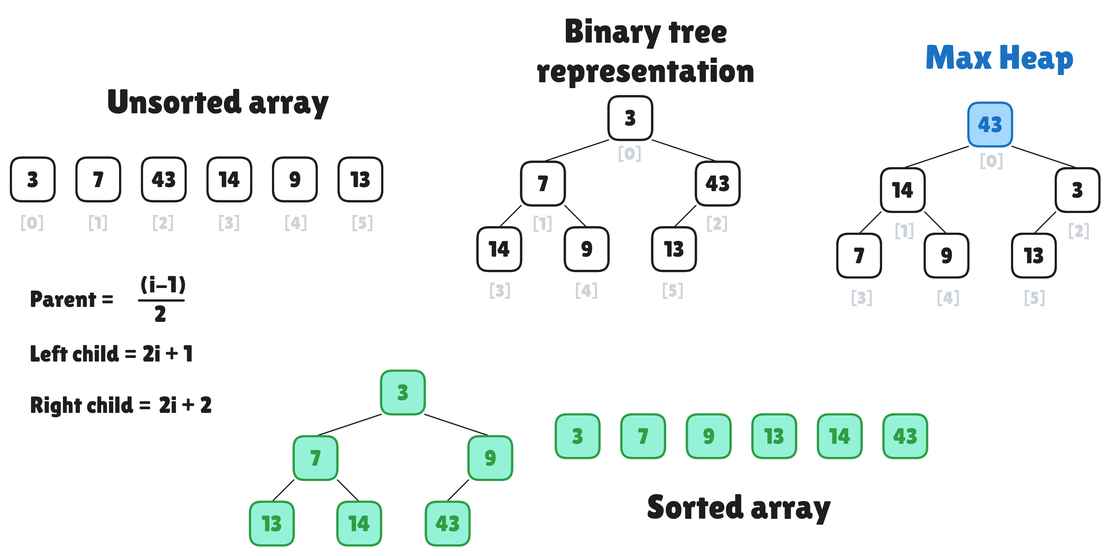
Heap Sort Algorithm
Heap Sort is a comparison-based sorting technique based on a Binary Heap data structure. It is similar to selection sort where we first find the maximum element and place it at the end. We repeat the same process for the remaining elements.
Read More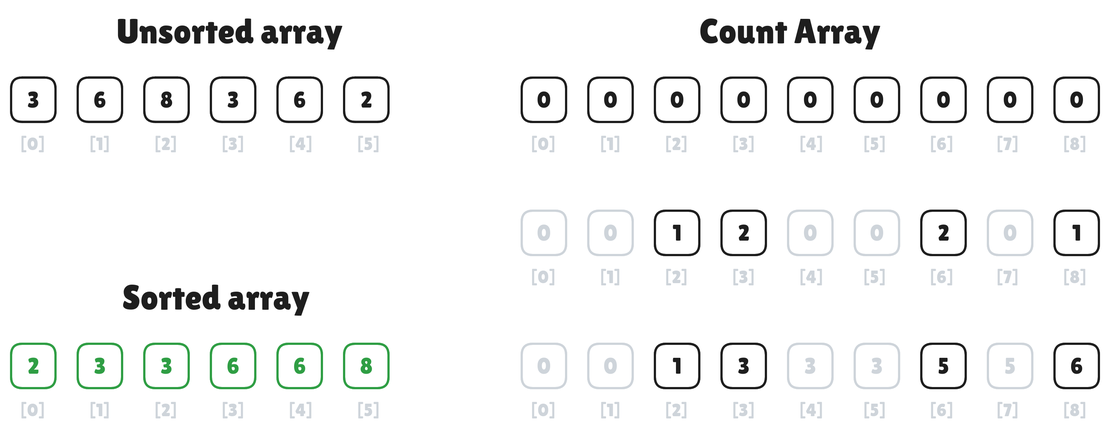
Counting Sort Algorithm
Counting Sort is a non-comparison-based sorting algorithm that operates with integer keys within a known, limited range. Unlike typical comparison sorts such as QuickSort or MergeSort, Counting Sort leverages the frequency of each element to achieve linear time sorting under suitable conditions. It is especially effective when the range of input values (k) is not significantly larger than the number of elements (n).
Read More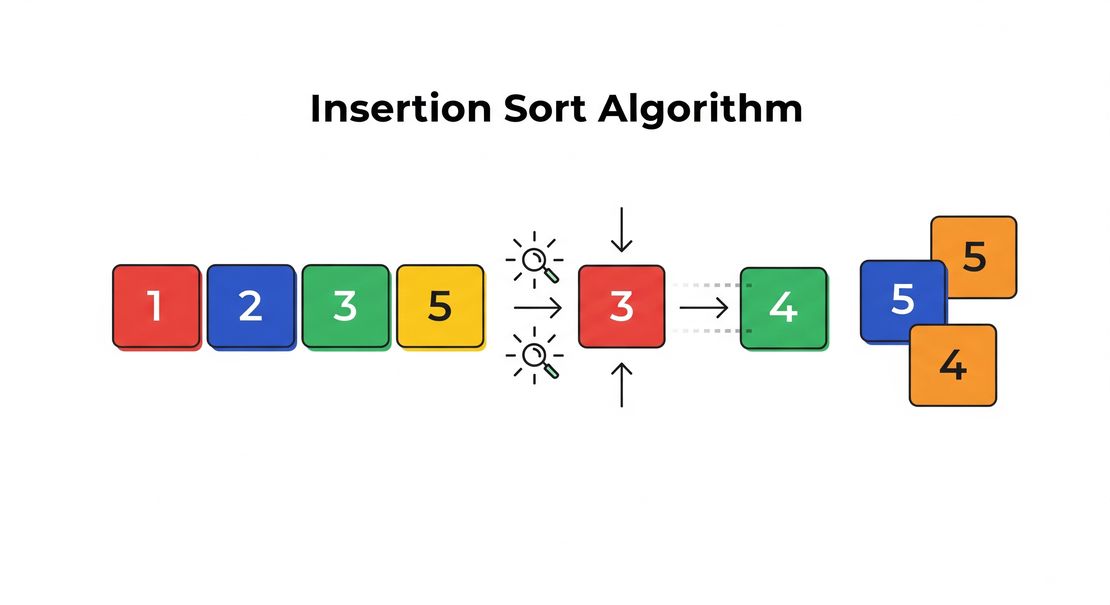
Insertion Sort Algorithm
Insertion Sort is a simple and intuitive comparison-based sorting algorithm. It builds the final sorted array one element at a time. It is much less efficient on large lists than more advanced algorithms such as quicksort, heapsort, or merge sort. However, it has advantages in simplicity and efficiency for small datasets.
Read More
Selection Sort Algorithm
Selection Sort is a simple comparison-based sorting algorithm. It works by dividing the input list into two parts: the sublist of items already sorted, which is built up from left to right, and the sublist of items remaining to be sorted that occupy the rest of the list. The algorithm proceeds by finding the smallest (or largest, depending on the sorting order) element from the unsorted sublist and swapping it with the leftmost unsorted element, moving the sublist boundaries one element to the right.
Read More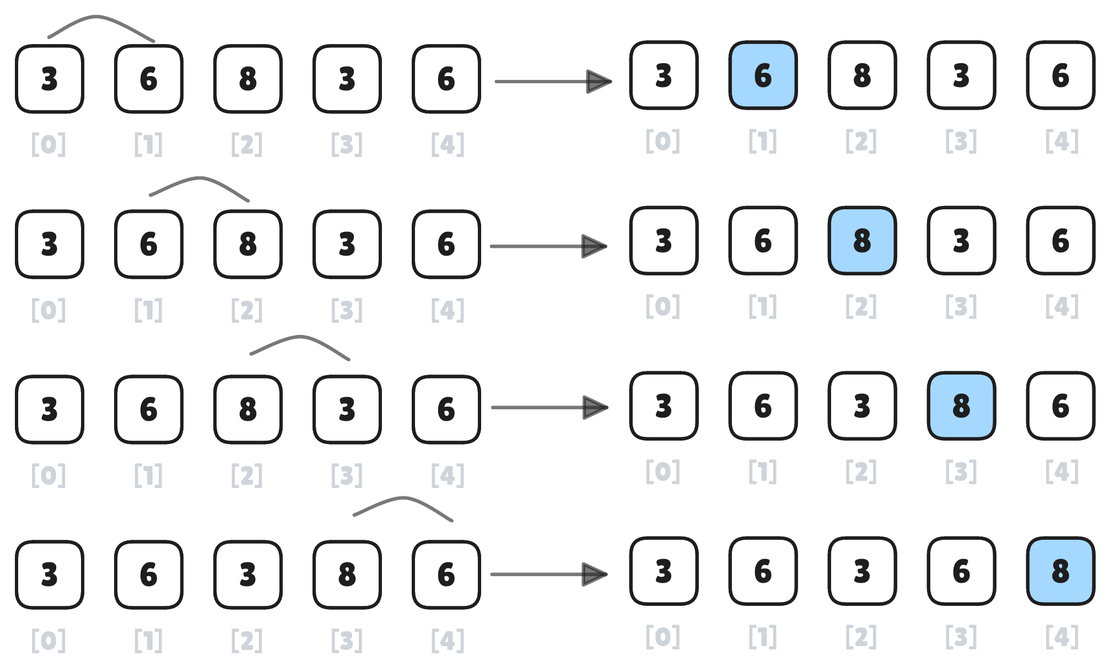
Bubble Sort Algorithm
Bubble Sort is one of the simplest sorting algorithms often taught as an introductory algorithm due to its intuitive approach. It repeatedly steps through the list, compares adjacent elements, and swaps them if they are in the wrong order. This process continues until the list is sorted.
Read More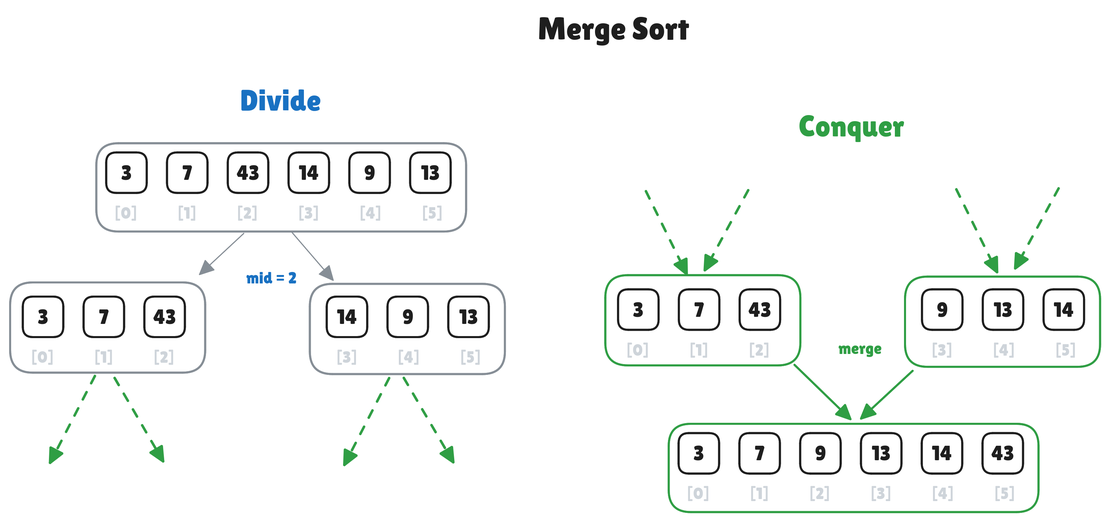
Merge Sort Algorithm
Merge Sort is a classical divide-and-conquer algorithm that efficiently sorts an array by recursively dividing it into two halves, sorting them independently, and then merging the sorted halves. It is one of the fundamental algorithms in computer science, often discussed in depth in books such as to Algorithms by Thomas H. Cormen et al.
Read More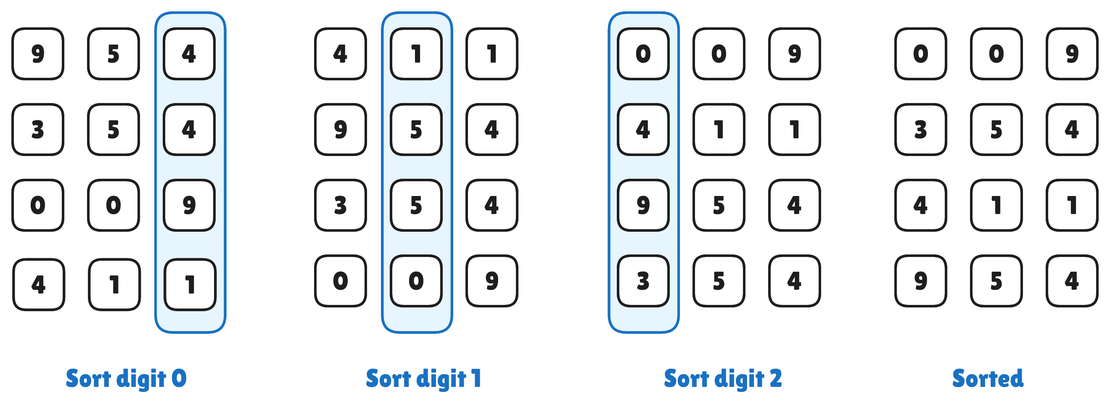
Radix Sort Algorithm: A Detailed Overview
Radix Sort is a non-comparative, integer sorting algorithm that sorts data with integer keys by grouping the keys by individual digits which share the same position and value. It processes each digit of the numbers, starting from the least significant digit (LSD) or most significant digit (MSD), depending on the implementation.
Read More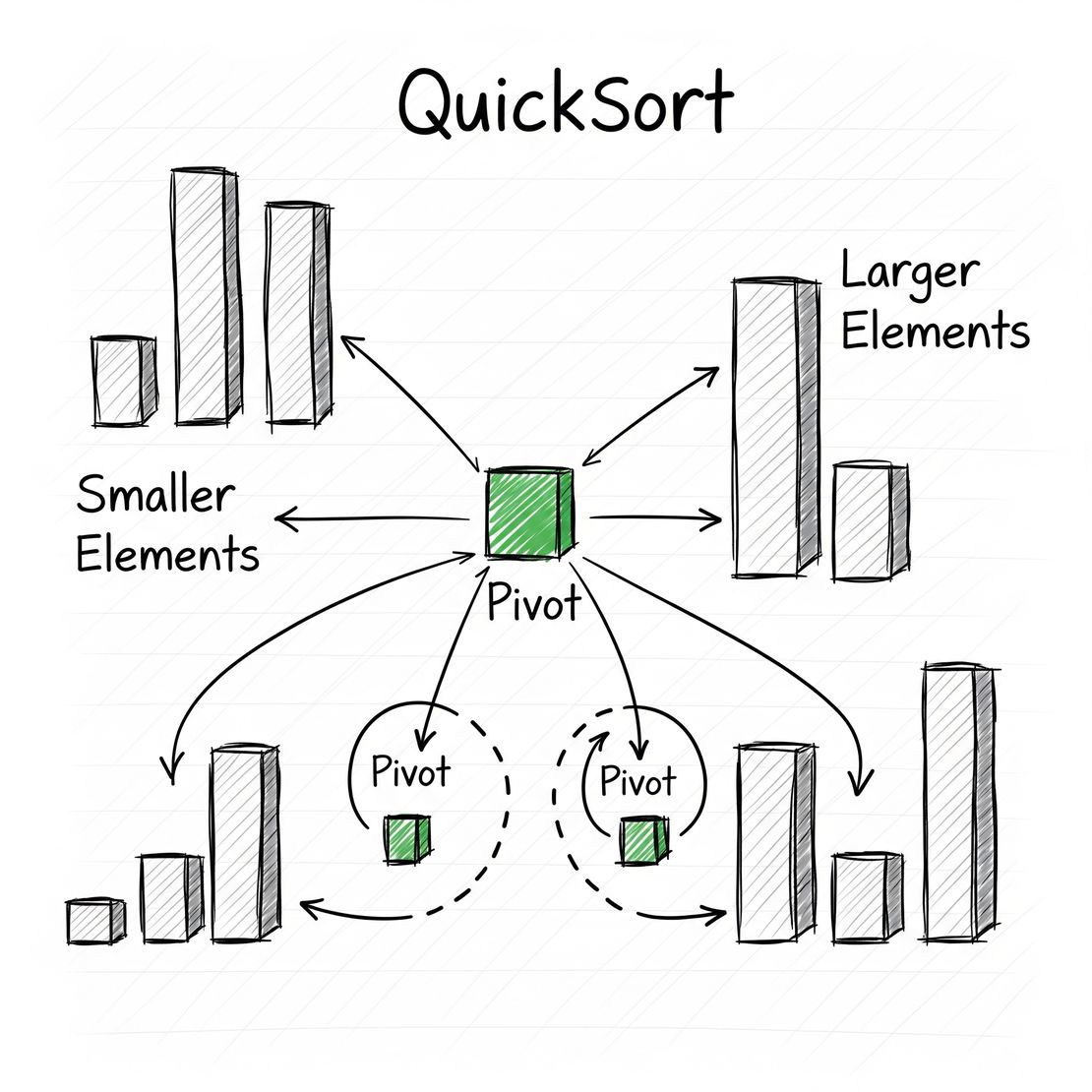
Quick Sort Algorithm: An In-depth Guide
Quick Sort is one of the most efficient and widely used sorting algorithms. Introduced by Tony Hoare in 1960, it employs a divide-and-conquer strategy to sort elements. It is particularly known for its performance in practice, often outperforming other sorting algorithms such as merge sort and bubble sort for large datasets.
Read More